WordPress’s the_tags Function Explained Using an Example
Posted on May 17, 2020
Table of Contents
This article will walk through a step-by-step explanation of how to use the WordPress function: the_tags.
Per the WordPress codex the syntax for the WordPress function for tags is as follows:
<?php the_tags( $before, $sep, $after ); ?>
If this is your first time seeing code like this, it may come off a little confusing.
Let’s make this easier to understand by using an example:
<?php the_tags('<span class="tag">', '</span><span class="tag">', '</span>'); ?>
The $before variable
In the example above, before each tag is an opening span tag <span class="tag"> is added. (To simulate a real-world example, we’re giving each tag a class of “tag” for styling purposes.)
This opening tag with the value of <span class="tag"> is what is assigned to the $before variable.
The $sep variable
Each tag is then separated with a closing tag </span> and another opening span tag <span="tag">. So, the value of </span><span class="tag"> is what is assigned to the $sep variable.
The $after variable
After all of the tags have been separated, the last tag in a list of tags is closed with the $after variable, which has a value of </span>.
Here’s How This Code Would Look If It Were Hardcoded In HTML
Let’s say we have three tags in one post. These tags are given class names of “Life Hacks”, “Productivity”, “Goals”.
Here’s what that code would look like if it were written out line by line using the example span tags above:
<span class="tag">Life Hacks</span>
<span class="tag">Productivity</span>
<span class="tag">Goals</span>
Make sense?
Breaking the_tags Down Further
It’s okay if it all doesn’t click with you right away. Let’s break it down again in a graphic using some labels and arrows.
Ok, so remember, this is the syntax for the_tags function:
<?php the_tags( $before, $sep, $after ); ?>
Now let’s break it down.
Here’s a neat graphic I made using Excalidraw:
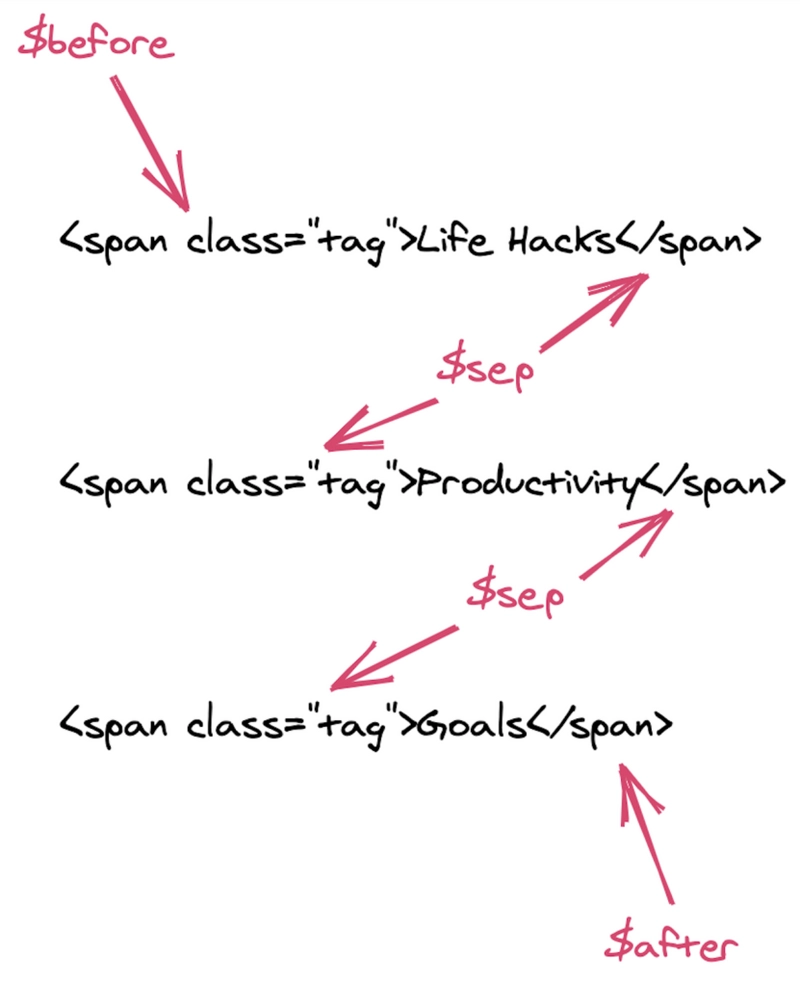
The $before variable is placed before the list of tags. Then, the $sep variable separates them. And finally, the $after variable closes the list of tags.